集合框架体系

ArrayList(jdk1.7)
基本结构
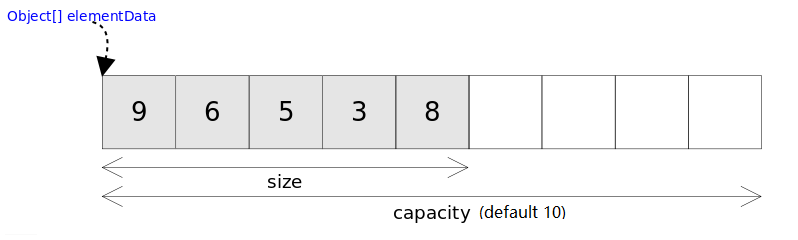
/** * Default initial capacity. */private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;/** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to * DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. */private transient Object[] elementData;/** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */private int size;初始化
三个构造方法。传入初始容量会直接设置数组大小,不传就设为空数组,或者传入Collection,转换并确保一下类型
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];}/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */public ArrayList() { super(); this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}/** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);}扩容机制
- 每当向数组中添加元素时,都要去检查添加后元素的个数是否会超出当前数组的长度。如果长度不足,将会进行扩容。(add方法中会调用ensureCapacityInternal -> ensureExplicitCapacity -> grow)
- grow方法是扩容操作的核心代码,可以看到,这个方法是先计算一个新的数组(新数组长度=原长+(原长>>1)),然后调用Arrays.copyOf方法将旧数组复制到新的数组中。
- 在添加大量元素前,可以使用ensureCapacity来手动增加ArrayList的容量,以减少递增式再分配的数量。
/** * Increases the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance, if * necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements * specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { int minExpand = (elementData != EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) // any size if real element table ? 0 // larger than default for empty table. It's already supposed to be // at default size. : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; if (minCapacity > minExpand) { ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); }}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity);}/** * The maximum size of array to allocate. * Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. * Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit */private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;/** * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}add
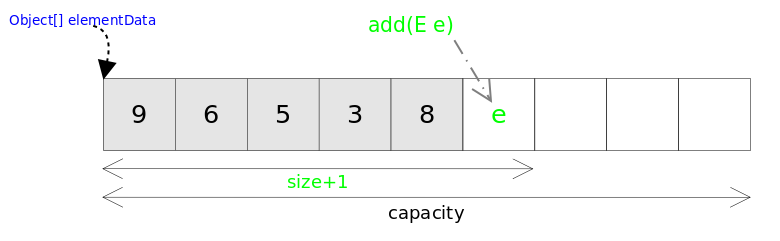
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true;}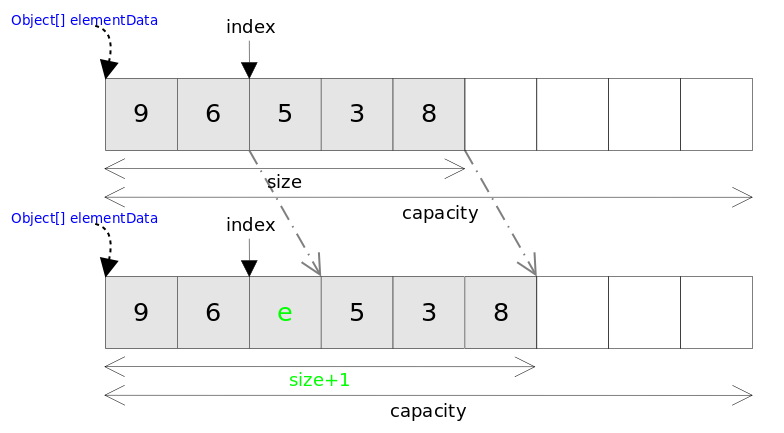
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++;}remove
删除操作是add()操作的逆过程,需要将删除点之后的元素向前移动一个位置。
需要注意的是为了让GC起作用,必须显式的为最后一个位置赋null值。
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue;}System.arraycopy
/** * 复制数组 * 本地方法,基于C实现,性能更高 * * @param src 原数组 * @param srcPos 原数据的起始位置 * @param dest 目标数组 * @param destPos 目标数组的起始位置 * @param length 要copy的数组长度 */public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);Vector(jdk1.7)
grow
与ArrayList不同的是,Vecotor根据步长来扩容
如果capacityIncrement大于0,则扩容为(+capacityIncrement),否则扩容两倍(+oldCapacity)
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}LinkedList(jdk1.7)
LinkedList同时实现了List接口和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作一个顺序容器,又可以看作一个队列(Queue),同时又可以看作一个栈(Stack)。 (不过,关于栈或队列,现在的首选是ArrayDeque,它有着比LinkedList(当作栈或队列使用时)有着更好的性能。)
基本结构
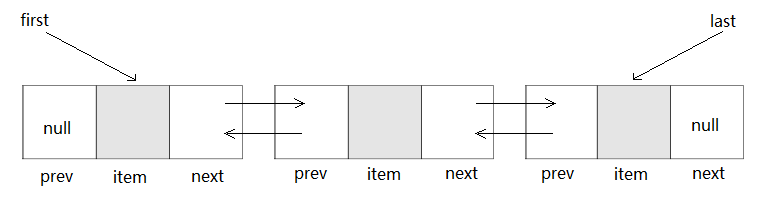
transient int size = 0;/** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */transient Node<E> first;/** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; }}add
addLast(E e)
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}. * * @param e the element to add */public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e);}
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true;}
void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;}add(int index, E element)
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index));} /** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. * Trick:由于链表是双向的,可以从开始往后找,也可以从结尾往前找 * 具体朝那个方向找取决于条件index < (size >> 1),也即是index是靠近前端还是后端 */Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; }}remove
/** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, * if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index * {@code i} such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list * changed as a result of the call). * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element */public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false;}/** * Unlinks non-null node x. */E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element;}clear
为了让GC更快可以回收放置的元素,需要将node之间的引用关系赋空。
/** * Removes all of the elements from this list. * The list will be empty after this call returns. */public void clear() { // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit // more than one generation // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++;}HashMap(jdk1.7)
基本结构
/** * 容量(capacity) * 必须是2的幂 而且小于2的30次方,默认为16 */static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;/** * 加载因子(loadFactor) * 默认为0.75,越大哈希冲突几率越大(链表更长) * 另外0.75作为默认值时,与容量相乘时绝对会得到整数 */static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;final float loadFactor;/** * 主干数组(table) */static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;/** * 键值对个数(size) */transient int size;/** * 扩容阈值(capacity * loadFactor) * 如果 table == EMPTY_TABLE 那么是initialCapacity * size大于此值时,会进行扩容 */int threshold;初始化
构造函数
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; init();}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);}public HashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);}第一次put时
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) inflateTable(threshold); //other code...}
/** * 扩容table */private void inflateTable(int toSize) { // Find a power of 2 >= toSize int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); table = new Entry[capacity]; initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);}
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) { // assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative"; return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;}
//Integer.highestOneBit//这返回了一个与i最接近的2的幂//jdk1.8中hashmap已将此方法直接称为tableSizeForpublic static int highestOneBit(int i) { // HD, Figure 3-1 i |= (i >> 1); i |= (i >> 2); i |= (i >> 4); i |= (i >> 8); i |= (i >> 16); return i - (i >>> 1);}get
/** * Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the * HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping * for the key. */final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); ////依次遍历冲突链表中的每个entry for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; //比较hash和key if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } return null;}
/** * 根据hash值求下标 * length为主干数组长度,也就是必然是2的幂 * 二进制为 00000100 00001000 00010000 * 减一就是 00000011 00000111 00001111(作为低位掩码) * 再进行位与&运算,hash值所有超过底位掩码的1都会被舍弃 * 这样,返回值范围就固定在了length-1 */static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; return h & (length-1);}
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; //more...}put
put方法首先会对map做一次查找,看是否包含,如果已经包含则直接返回
否则会通过addEntry方法插入新的entry,插入方式为头插法。
/** * Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to * the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this * method to resize the table if appropriate. * * Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method. */void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { //size超过阈值并且所要插入的下标不为空,则会进行扩容 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);}/** * Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries * as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning, * deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table. * * Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map), * clone, and readObject. */void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++;}transfer造成的链表成环
- 当两个线程同时插入元素,并且同时发现需要扩容时,由于扩容时会改变链表元素的顺序,在线程1未完成扩容的时候,线程2抢占到了资源完成了扩容
- 这时线程1继续执行,由于线程1中有一个临时变量e,它的next会被指向新数组的一个元素,此时继续执行会造成错误的赋值,导致链表成环。
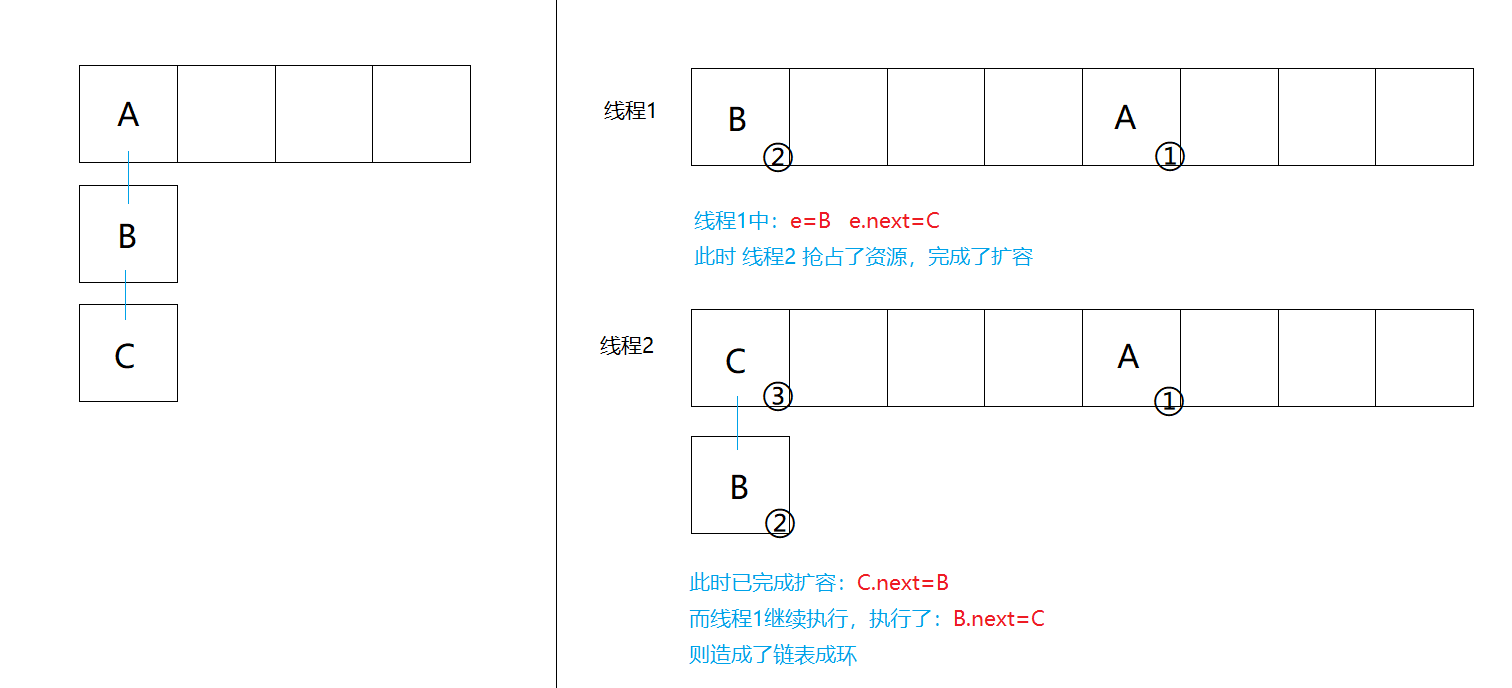
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { //e为空时循环结束 while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; // 记录oldhash表中e.next if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); // rehash计算出数组的位置(hash表中桶的位置) // 成环的代码主要是在这三行代码 // 首先插入是从头开始插入的 e.next = newTable[i]; // e要插入链表的头部, 所以要先将e.next指向new hash表中的第一个元素 newTable[i] = e; // 将e放入到new hash表的头部 e = next; // 转移e到下一个节点, 继续循环下去 } }}Hashtable(jdk1.7)
和HashMap的不同
- 构造函数中直接初始化table
- Hashtable默认的容量是11。
- 下标使用取模操作
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; - 每次扩容,容量变为原来的2n+1,
(oldCapacity << 1) + 1 - key和value都不能为空
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: " + loadFactor); if (initialCapacity==0) initialCapacity = 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor; table = new Entry[initialCapacity]; threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); initHashSeedAsNeeded(initialCapacity);}
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);}
//默认的initialCapacity是11public Hashtable() { this(11, 0.75f);}/** * Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this * hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more * efficiently. This method is called automatically when the * number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity * and load factor. */protected void rehash() { int oldCapacity = table.length; Entry<K,V>[] oldMap = table; // overflow-conscious code int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) // Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets return; newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } Entry<K,V>[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity]; modCount++; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); boolean rehash = initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity); table = newMap; for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) { for (Entry<K,V> old = oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) { Entry<K,V> e = old; old = old.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = hash(e.key); } int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity; e.next = newMap[index]; newMap[index] = e; } }}HashMap(jdk1.8)
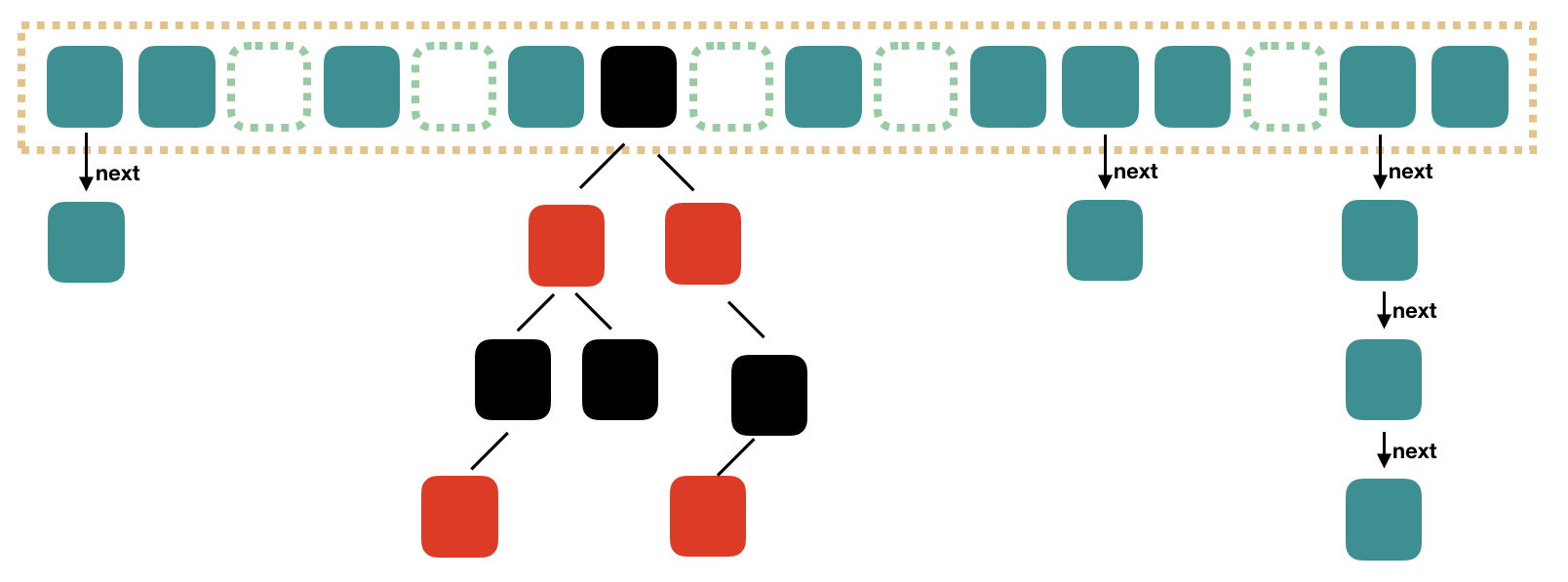
什么情况下从链表转为红黑树?
当Map链表长度大于或等于阈值(默认为 8)并且还满足容量大于或等于 MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认为 64)的要求,就会把链表转换为红黑树。 当红黑树的节点小于或等于 6 个以后,会恢复为链表。
- 为什么是8? 服从0.5的泊松分布 每个bucket有0个元素的概率是0.6,1是0.3,2是0.07,8是亿分之六 因此链表长度超过 8 是几乎不可能的
ConcurrentHashMap(jdk1.7)
jdk1.7使用 分段锁机制 实现 jdk1.8使用 数组+链表+红黑树+CAS原子操作 实现
基本结构
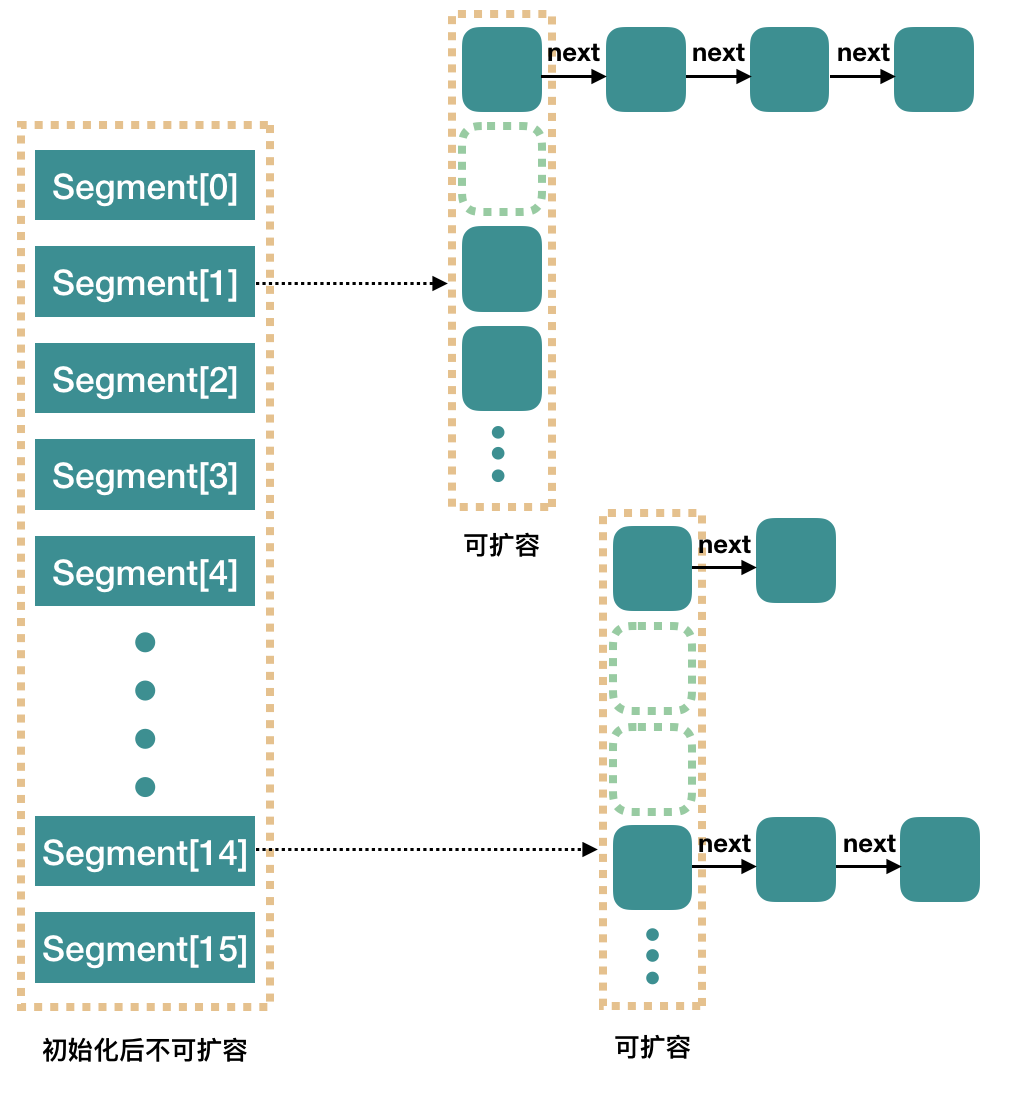
/** * 并发级别(concurrencyLevel),实际上就是Segment的数量,默认16 * 理论上,可以同时支持 16 个线程并发写,只要它们的操作分布在不同的 Segment 上。 */static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;/** * segments[i]中的table的容量 */static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;/** * Mask value for indexing into segments. The upper bits of a * key's hash code are used to choose the segment. */final int segmentMask;/** * Shift value for indexing within segments. */final int segmentShift;/** * final修饰的Segment数组,不可扩容 */final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
/** * 哈希表的特殊版本。这个ReentrantLock的子类只是为了简化一些锁并避免单独的构造。 */static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; //more...}
static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; //more...}快速失败fail-fast
快速失败机制,是java集合中的一种错误检测机制。当在迭代集合的过程中该集合在结构上发生改变的时候,就有可能会发生fail-fast,即抛出 ConcurrentModificationException异常。
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr();}
/** * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr */private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // 遍历过程中的【即将遍历】的元素的索引 int lastRet = -1; // 记录【刚刚遍历】的元素的索引,不存在上一个时,为-1 int expectedModCount = modCount; //fail-fast判断的关键变量, //初始值为ArrayList中的modCount(操作数) //请看最下方的checkForComodification方法
public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; }
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; }
public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
@Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); }
/** * expectedModCount只在遍历开始的时候被赋予了modCount的值 * 如果有程序修改了modCount,就会抛出 并发修改异常 */ final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); }}
评论